Factors Influencing International Property Values
Understanding the dynamics that shape international property values is crucial for anyone involved in global real estate. Whether considering an overseas home acquisition, a substantial commercial investment, or simply observing global economic trends, a multitude of factors converge to determine the worth of land and buildings across different nations and regions. These influences range from broad economic indicators to specific local characteristics, creating a complex but discernible landscape for property valuation worldwide. Navigating this intricate environment requires an awareness of both macro-level forces and micro-level details that collectively contribute to an asset's market standing and potential for growth.
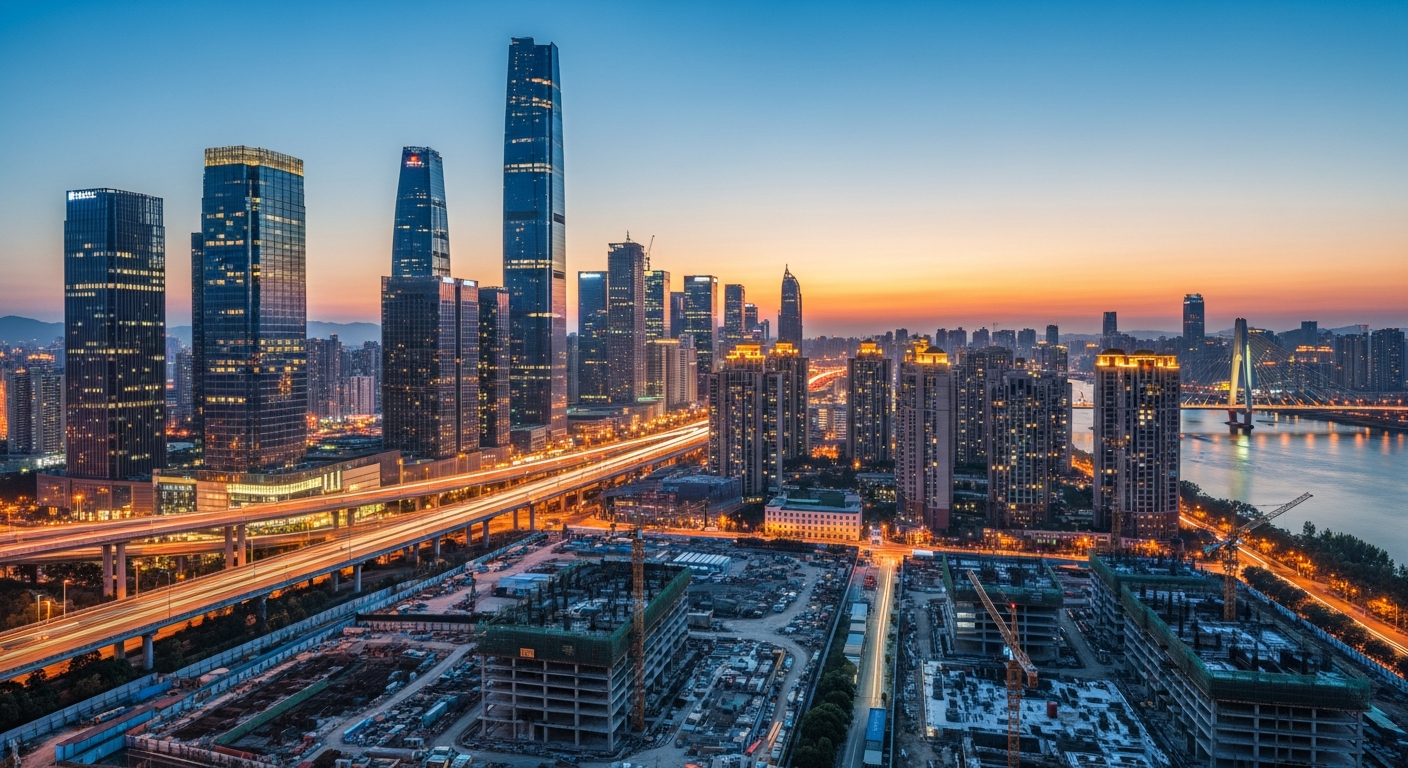

Economic and Market Dynamics Affecting Property
Global economic conditions play a significant role in influencing international property values. Factors such as a country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth, inflation rates, interest rates, and employment levels directly impact the purchasing power of individuals and businesses, thereby affecting demand for both residential and commercial property. Strong economic performance typically leads to increased consumer confidence and investment, driving up real estate values. Conversely, economic downturns can lead to reduced demand and a depreciation in asset worth. The overall health of the financial market, including the availability of credit and lending policies, also dictates the ease and cost of property acquisition, further influencing market activity and pricing.
International investment flows are another critical component. When foreign capital enters a market, it can stimulate development and push up property values, particularly in prime urban areas. Currency exchange rates also factor into this, making properties in certain countries more or less attractive to international buyers depending on the strength of their home currency. Government policies, including taxation on foreign ownership, property transfer taxes, and regulations on capital repatriation, can either encourage or deter cross-border real estate investment, directly impacting the global property market.
Urban Development and Infrastructure’s Role
The level and quality of urban development and infrastructure are fundamental drivers of property value. Cities with robust infrastructure, including efficient transportation networks (roads, public transit, airports), reliable utilities (water, electricity, internet), and essential public services (healthcare, education), tend to command higher property prices. These elements enhance livability and operational efficiency for businesses, making locations more desirable for both residential and commercial purposes. Planned development projects, such as new business districts, residential complexes, or major public works, can significantly appreciate the value of surrounding land and existing buildings by improving accessibility and amenities.
Sustainable and smart urban planning initiatives, which focus on green spaces, energy efficiency, and technological integration, are increasingly becoming valuation factors. Areas that invest in future-proof infrastructure and foster a high quality of life often attract long-term investment and a stable population base, underpinning consistent property value growth. Conversely, a lack of investment in infrastructure or unchecked urban sprawl can depress property values by reducing desirability and increasing living costs or commute times.
Understanding Property Types and Ownership Structures
The specific type of property—whether residential, commercial, or industrial—has distinct valuation drivers. Residential property values are often influenced by population growth, household income, local amenities, and housing supply. Commercial property, encompassing offices, retail spaces, and hospitality venues, is more closely tied to business activity, economic growth, and rental yields. Industrial land and buildings are valued based on factors like logistical access, proximity to markets, and suitability for manufacturing or warehousing operations. Each segment responds differently to economic shifts and local market conditions.
Ownership structures and legal frameworks also play a pivotal role in international property acquisition and valuation. Different countries have varying laws regarding foreign ownership, leasehold versus freehold tenure, and property rights. Clarity and stability in these legal frameworks reduce investment risk and can attract more global capital. The ease of property transfer, registration processes, and dispute resolution mechanisms can significantly affect an asset’s liquidity and attractiveness to international investors, ultimately impacting its perceived and actual value within a global portfolio.
Valuation Methodologies and Portfolio Management
Property valuation is a multifaceted process that considers various approaches, including comparable sales analysis, income capitalization, and replacement cost methods. For international property, these methodologies must be adapted to local market nuances, data availability, and regulatory environments. Accurate valuation is crucial for making informed investment decisions, managing a diverse portfolio, and assessing financial risk. Global real estate trends, such as the increasing demand for sustainable buildings or the rise of co-working spaces, also influence how properties are valued and positioned within a portfolio.
Effective portfolio management in international real estate involves diversifying across different geographies, property types, and risk profiles to mitigate market-specific downturns. Investors often seek to balance high-growth emerging markets with more stable, mature markets. Understanding the interplay between local supply and demand, global capital flows, and geopolitical stability is essential for optimizing a real estate portfolio’s performance and ensuring long-term asset appreciation. The ongoing analysis of these factors allows investors to adapt their strategies to evolving market conditions and capitalize on emerging opportunities across the globe.
In conclusion, international property values are shaped by a complex interplay of economic forces, urban development, specific property characteristics, and legal frameworks. A comprehensive understanding of these factors, from global economic trends and financial market conditions to local infrastructure quality and ownership laws, is essential for accurate valuation and strategic investment. As global economies continue to evolve, so too will the landscape of international real estate, necessitating continuous analysis and adaptation from investors and stakeholders worldwide.